Bronchiolar adenoma (BA) is a newly designated rare entity of the lung, which is characterized by bilayered bronchiolar-type epithelium with a continuous layer of basal cells. These include bronchiolar epithelial (atypical) hyperplasia, glandular papillary tumor and ciliated muconodular papillary tumor of the peripheral lung (CMPT). Due to its complexity and low incidence rate, the understanding of the pathological nature of this kind of disease and the name of pathological diagnosis were confused. In 2018, Chang et al.1 first defined the concept of BA. Based on the composition of surface cells, it is divided into proximal‐type BA and distal‐type BA, there are also some cases of incomplete or absent basal cells. Cases with certain cell atypia were included in the non-classical bronchial adenoma.
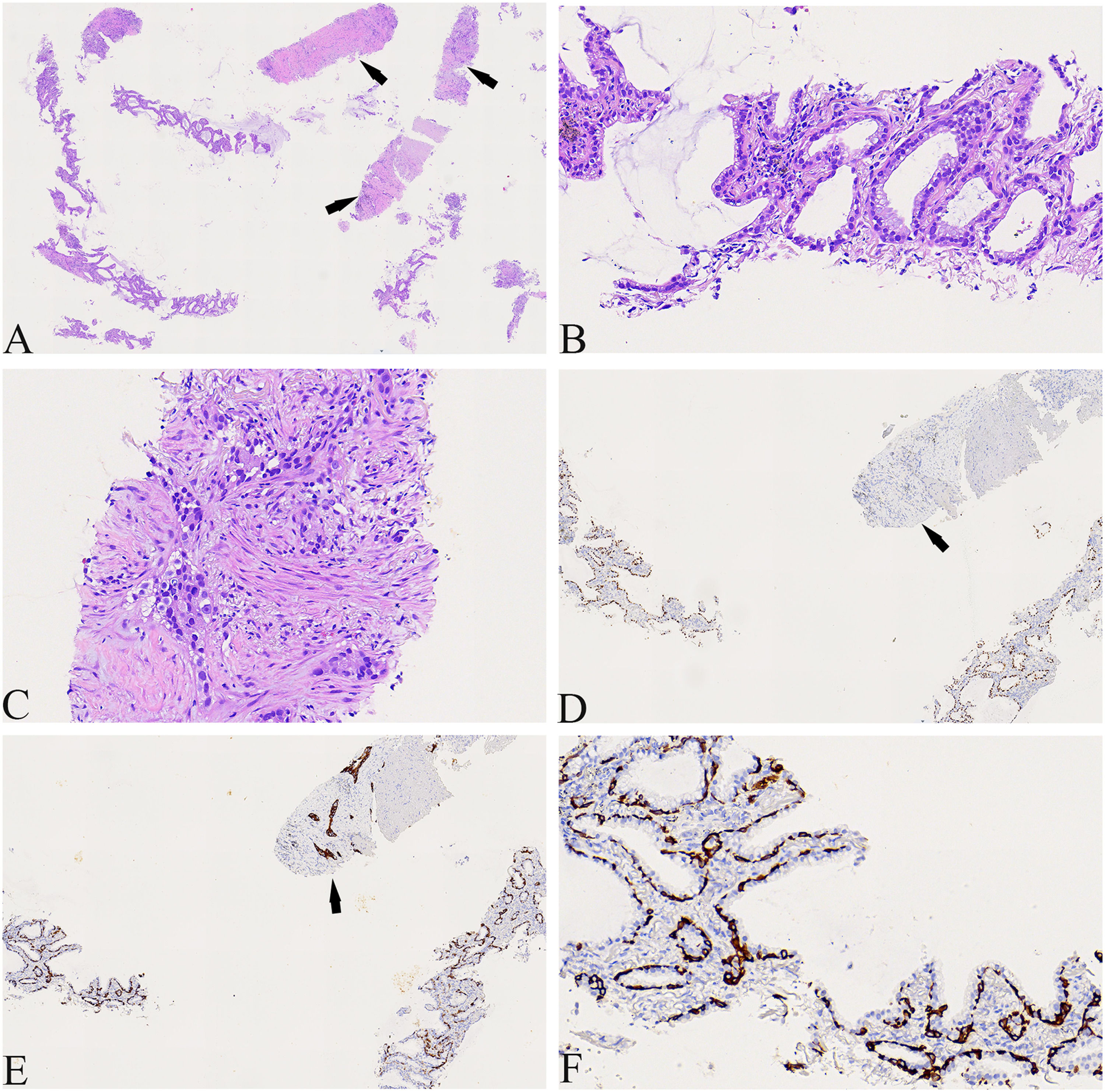
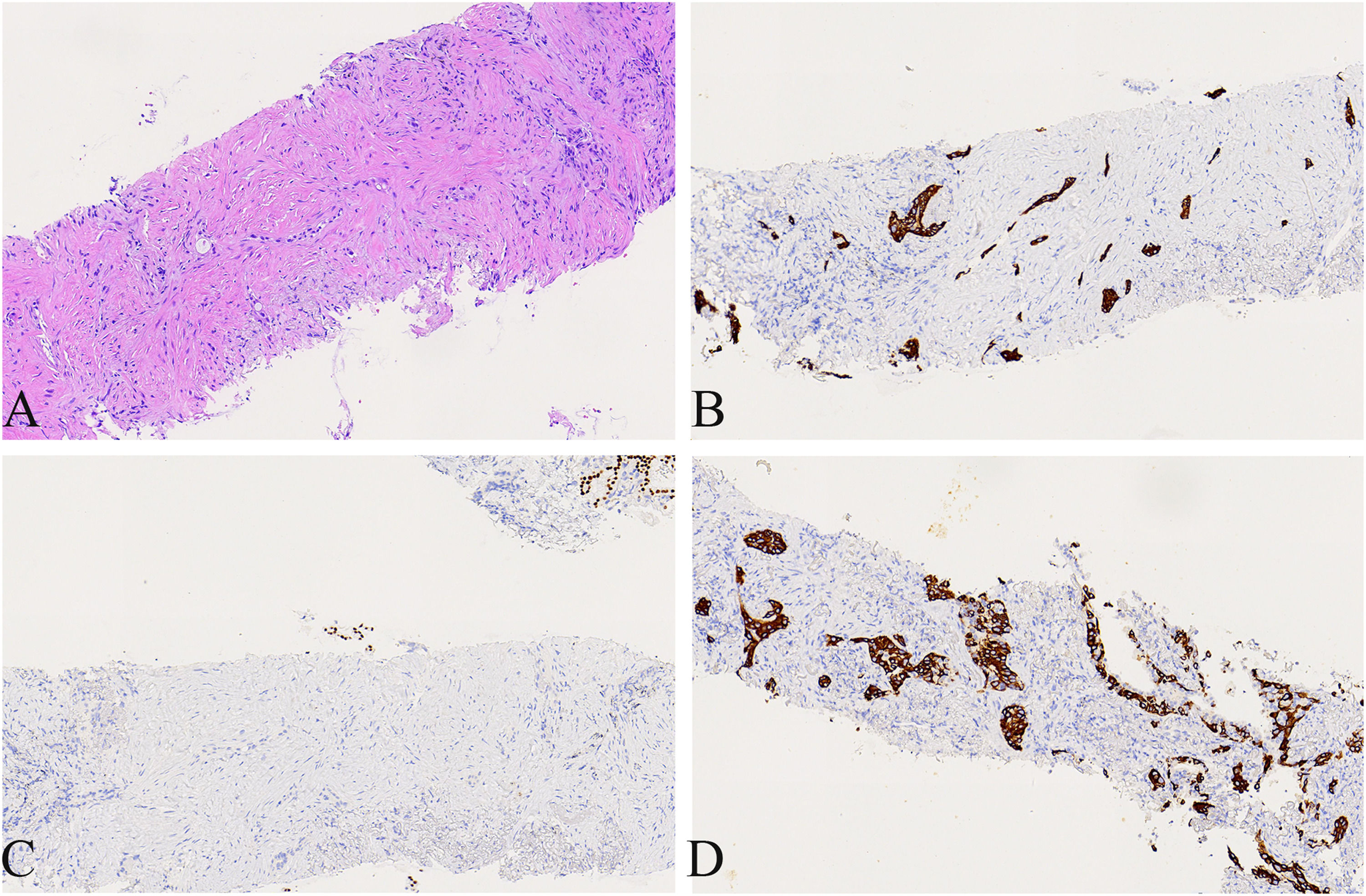
A 74-year-old male patient with a history of smoking for 30 years was admitted to the hospital with left side paroxysmal dull pain, cough and weight loss of 10KG without obvious inducement. Computed tomography (CT) showed a lumpy mass in the posterior segment of the left upper lobe tip, about 48mmx41mm in size, with lobed and burr signs, indistinct from the pleura, uneven medium to obvious enhancement, embedding the proximal segment of the left upper pulmonary artery, and local osteolytic bone destruction near the left posterior ribs 3rd and 4th. Past history and family history are unremarkable. The physical examination revealed no other obvious abnormalities. Serum levels of infection, inflammatory and tumor markers were all within the normal range, and only carcinoembryonic antigen was measured at 7.05 ng/mL (the reference value is less than 4.5 ng/mL). The patient underwent a lung needle aspiration biopsy. Histologically, part of the tumors was shown flat (glandular) architecture and was composed of bilayered cellular elements with luminal epithelial cells and subjacent basal cells (Fig. 1A).The luminal cells were mainly mucous cells and ciliated cells (Fig. 1B). TTF-1 (Fig. 1D) and NapsinA were expressed in the luminal epithelial cells of this region. CK5/6 (Fig. 1E,F) and p63 were expressed in the surrounding basal cells. In addition, some tumor cells showed solid irregular small clumps in stromal infiltrate growth, accompanied by fibrostromal reaction (Figs. 1C, 2A). In this area, tumor cells expressed p40 and CK5/6 (Figs. 1E, 2B), but did not express TTF-1 (Figs. 1D, 2C) NapsinA and p53 showed mutant-type. In the focal area, basal cells budding around the glandular cavity, gradually transitioning to interstitial infiltrating growth (Fig. 2D). Based on the above findings, the pathological diagnosis was bronchial adenoma malignant transformation into squamous cell carcinoma.
(A) The tumors were shown flat (glandular) architecture (Left side of image) and part of the tumors cells (as indicated by the arrow) showed solid irregular small clumps in stromal infiltrate growth (×40). (B) Local magnification of Fig. A, the luminal cells was mainly mucous cells and ciliated cells(×400). (C) Local magnification of Fig. A, the tumors cells showed solid irregular small clumps in stromal infiltrate growth, accompanied by fibrostromal reaction (×400). (D) TTF-1 was expressed in luminal epithelial cells, but not in solid growth areas as shown by the arrows(×100). (E) CK5/6 was only expressed in periglandular basal cells and strongly expressed in solid growth regions as shown by the arrows (×100). (F) Local magnification of Fig. 1E, CK5/6 was only expressed in periglandular basal cells(×400).
(A) Local magnification of Fig. 1 A, the tumors cells showed solid irregular small clumps in stromal infiltrate growth, accompanied by fibrostromal reaction(×200). (B) CK5/6 was expressed in solid growth regions(×200). (C) TTF-1 was not expressed in solid growth (×200). (D) Basal cells budding around the glandular cavity, gradually transitioning to interstitial infiltrating growth(×200).
BA/CMPT is a rare lung tumor characterized by nodular proliferation of bilayered bronchiolar-type epithelium with a continuous layer of basal cells. BA is considered a benign neoplasm. Recently, some cases of driver mutations or malignant transformations have been reported. However, the nature of BA/CMPT remains controversial. Chen et al.2 reported a case of mucinous adenocarcinoma(MA) resulting from CMPT, and speculated that CMPT was a precursor of MA. Lau et al.3 proposed that CMPT is a precursor of MA based on the multistage pathogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma. To date, there are only a few articles that describe the squamous metaplasia of BA. Recently, Li et al.4 reported a case of multiple pulmonary BA with squamous metaplasia and budding growth, and suggested that it had the potential to transform into squamous cell carcinoma.We used H&E staining and immunohistochemistry to diagnose our patient as having squamous cell carcinoma caused by the malignant transformation of BA, thus providing histological evidence of the malignant potential of BA, expanding its connection with malignant transformation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of BA transforming into squamous cell carcinoma.
Ethical considerationsWritten informed consent was obtained from the participant for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Sichuan Mianyang 404 Hospital.
Funding informationNone.
Consent from all authorsAll authors reviewed this manuscript and agreed to submit this manuscipt.
CRediT authorship contribution statementNing Zhou: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. Ying Chen: Writing – original draft, Data curation. Shuya Hu: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. Zhengfang Jiang: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
CRediT authorship contribution statementNing Zhou: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. Ying Chen: Writing – original draft, Data curation. Shuya Hu: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. Zhengfang Jiang: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.