In patients with severe acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) the prone position has been shown to improve survival of patients who are severely hypoxemic with an arterial oxygen tension to inspiratory oxygen fraction ratio (PaO2/FiO2)<100. In those patients tracheobronchial toilette is crucial in preventing or treating airways obstructed by secretions and deterioration of oxygenation. Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy is widely recognized as an effective technique to perform bronchial toilette in the intensive care unit (ICU).
Flexible bronchoscopy performed during prone mechanical ventilation in two cardiosurgical patients who developed ALI after complex surgery, proved feasible and safe and helped to avoid undesirable earlier cessation of prone mechanical ventilation. However decision making about bronchoscopy in severe hypoxia should be even more cautious than in the supine patient, as dangerous delay in resuscitation manoeuvres due to postponed switching the patient to the supine position should always be prevented.
Em pacientes com lesão pulmonar aguda grave (LPA) ou síndrome de dificuldade respiratória aguda (ARDS), foi demonstrado que a posição de decúbito ventral melhora a sobrevivência de pacientes que sejam gravemente hipoxémicos com uma relação entre a pressão de oxigénio no sangue arterial e a fração inspirada de oxigénio (PaO2/FiO2) <100. Nesses pacientes, a toilette traqueobrônquica é fundamental para a prevenção ou tratamento das vias respiratórias obstruídas por secreções e a deterioração da oxigenação. A fibrobroncoscopia flexível é amplamente reconhecida como uma técnica eficaz para realizar a toilette brônquica na unidade de cuidados intensivos (UCI). A broncoscopia flexível realizada durante a ventilação mecânica em posição de decúbito ventral em 2 pacientes de cirurgia cardíaca que desenvolveram LPA após cirurgias complicadas, provaram ser viáveis e seguras, e ajudaram a evitar uma interrupção precoce indesejável da ventilação mecânica em posição de decúbito ventral. No entanto, a tomada de decisão sobre a broncoscopia em caso de hipóxia grave deve ser ainda mais cautelosa do que no paciente em posição supina, dado que um atraso perigoso nas manobras de reanimação devido à mudança adiada do paciente para a posição supina deve ser sempre evitado.
In patients with severe acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) the prone position during mechanical ventilation has been shown to be able to recruit lung parenchyma and to favour protective mechanical ventilation, resulting in improved survival even in severely hypoxemic patients with an arterial oxygen tension to inspiratory oxygen fraction ratio (PaO2/FiO2)<100.1 However prolonged sessions are required in order to obtain advantages,2 during which the prone position gives enhanced mobilization of airway secretions through postural drainage and lung recruitment.
Suctioning is therefore crucial for tracheobronchial toilet. However when standard tracheal suctioning results are not satisfactory, and arterial desaturation occurs, this usually prompts the intensivist to switch the patient to the supine position in order to get improved tracheobronchial suctioning. This means an earlier interruption of the prone ventilation with a loss of the positive respiratory effects which are gained when there is the full prone cycle.
Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy is widely recognized as an effective technique in removing retained airway secretions and improving atelectasis in a variety of clinical conditions, including bronchial toilette and bronchoalveolar lavage in the intensive care unit (ICU).3
No data are available on how and whether fiberoptic bronchoscopy could help prevent prolonged prone position ventilation sessions from being interrupted, earlier than scheduled, with potential detrimental therapeutic effects.
We describe bronchial toilette by flexible bronchoscopy performed during prone mechanical ventilation in two cardiosurgical patients who developed ALI after combined coronary artery surgery, aortic valve replacement and carotid endoarterectomy.
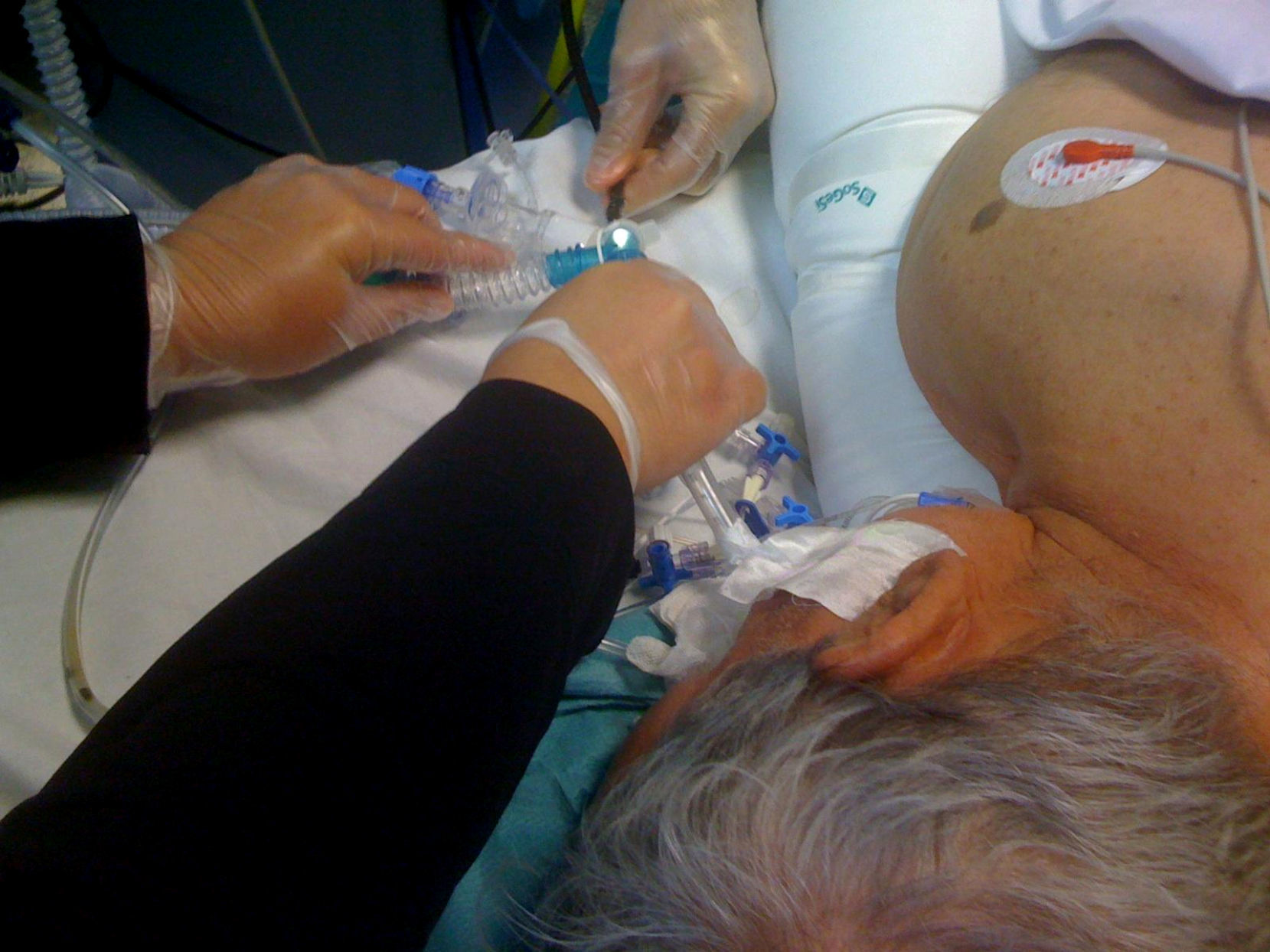
Case reportCase 1A 75-year-old lady, although extubated uneventfully on the first postoperative day, on the second postoperative day she showed dyspnoea, a PaO2/FiO2 ratio of 70 and SaO2<92% which required tracheal reintubation and mechanical ventilation. After 24h of ineffective protective mechanical ventilation in Biphasic Intermittent Airway Pressure (BiPAP, Drager, Lubeck, Germany) modality with FiO2 0.7, respiratory rate (RR) 18breath/min, I/E ratio 1:1, peak airway inspiratory pressure 25cmH2O and PEEP 10cmH2O, prone ventilation was applied with immediate rise in SaO2>98%. The patient was passive and completely controlled by ventilation. Five hours after starting the prone session, an acute deterioration of SaO2<88% was observed. Arterial blood gas analysis (ABG) showed hypoxaemia and metabolic acidaemia due to secondary cardiovascular impairment (pH 7.21, PaO2 65mmHg, PaCO2 48mmHg and HCO3 20mEq/l). Clinical examination through auscultation showed airways obstruction due to secretions. Tracheal suctioning through a closed circuit aspiration system and also a larger tube through a standard catheter mount was only partially effective and the SaO2 remained <92%. Therefore we performed flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy while the patient maintained the prone position by inserting the bronchoscope through the elbow port of the catheter mount (Fig. 1) into the endotracheal tube. During the procedure FiO2 was raised to 1.0 while PEEP and respiratory frequency were reduced to avoid a possible increase in intrinsic PEEP (PEEPi). Simultaneously, peak airway inspiratory pressure was increased to maintain an expiratory minute ventilation equal to what it had been before the bronchoscope insertion. PEEPi was measured by achieving an end expiratory hold pause, after this the bronchoscopy ventilatory settings were reset to the previous BiPAP modality. The bronchoscopy revealed the presence of a clot obstructing the lower left bronchus lumen which was removed, resulting in rapid recovery of oxygenation (SaO2>98% pH 7.27, pO2 122mmHg, pCO2 43mmHg).
Case 2A 75-year-old lady was treated with prone mechanical ventilation in Biphasic Intermittent Airway Pressure (BIPAP, Drager, Lubeck, Germany) modality for early postoperative ARDS. Ventilator setting was RR 18breath/min, I/E ratio 1:1, peak airway inspiratory pressure<26cmH2O, PEEP 10–15cmH2O and FiO2 0.8. On the third postoperative day, during a prone session with the patient passive and completely controlled by ventilation, a sudden drop in SaO2 occurred. ABG showed pH 7.19 pO2 61mmHg, pCO2 56mmHg and HCO3 18mEq/l. Clinical examination through auscultation showed that airways were obstructed by a large amount of secretions. Tracheal suctioning resulted in unsatisfactory SaO2 improvement and auscultation still confirmed that the airways were obstructed by secretions, therefore a selective bronchial toilet was deemed necessary. A flexible bronchoscopy was then carried out in the prone position as described in the first case. Ventilator parameters were set as mentioned above. A large amount of secretions were suctioned in the lower lung regions with quick normalization of SaO2 and ABG values (pH 7.30 pO2 116mmHg pCO2 45mmHg). Previous ventilatory settings were restored after the procedure.
Both patients were discharged home alive from the hospital.
DiscussionThis preliminary experience suggests that flexible bronchoscopy in the patient undergoing mechanical ventilation in the prone position is feasible and safe. Most importantly such endoscopic technique helps to avoid undesirable premature interruption of the prone mechanical ventilation and the consequent loss of the favourable physiological gains, which had the potential to achieve, atelectasis of the lung regions recruited while prone, increased intrapulmonary shunt, decreased SaO2 and increased pulmonary artery resistances. To date there are no guidelines for the ventilator setting during fiberoptic bronchoscopy. Great care must be taken when bronchoscopy is performed on a patient receiving mechanical ventilation. Extremely low VT and significant PEEPi may develop unless flow, respiratory rate, mode, and tube size are carefully selected.4 We increased FiO2 to 1, reduce PEEP level and respiratory frequency to avoid an increase in PEEPi. At the same time inspiratory pressure was increased to maintain minute volume and avoid an increase in carbon dioxide
Although performing flexible bronchoscopy in the prone position patient does not seem to make the procedure more difficult when compared to the supine position, decision making about bronchoscopy in severe hypoxia should be even more cautious than in the supine patient, as a dangerous delay in resuscitation manoeuvres due to postponed switching the patient to the supine position should always be avoided. In addition ventilator parameters must be appropriately set to prevent oxygen desaturation and pulmonary hyperinflation due to the severe reduction in the internal diameter of the endotracheal tube. It could be worth carrying out a randomized controlled trial to investigate the impact of such an approach on the outcome of critically ill patients undergoing prone mechanical ventilation.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.